
英语原文共 10 页,剩余内容已隐藏,支付完成后下载完整资料
标题
Understanding the determinants of demand for public transport : Evidence from suburban rail operations in five divisions of Indian Railways
了解公共交通需求的决定因素: 从印度郊区铁路运营的五个部分来看
作者
Syed Rahman a , Chandra Balijepalli b, n
a Indian Railway Traffic Service, Indian Railways, South Eastern Railway, Kolkata 700043, India
b Institute for Transport Studies, University of Leeds, Leeds LS2 9JT, England, United Kingdom
article info 文章信息
Article history:
Received 19 January 2015
Received in revised form 9 February 2016
Accepted 20 February 2016
文章历史:
于2015年1月19号收到初稿
于2016年2月9号收到修订稿
于2016年2月20号接收文章
Keywords:
Fare elasticity
Demand for public transport
Suburban rail operations in India
Static/dynamic modelling
Bootstrapping
关键词:
票价弹性
公共交通需求
印度郊区铁路运营
静态/动态建模
引导
Abstract
This paper analyses suburban rail fare elasticity and compares the results across five suburban divisional operations of the Indian Railways in three cities viz., Chennai, Kolkata and Mumbai. The three cities chosen have a highly varying modal share of public transport trips and thus offer interesting insights into the attitudes of trip makers towards the changes in operational variables such as fares, service levels. This paper contributes towards understanding of the determinants of demand for public transport in a developing country and applies econometric methods involving static and dynamic modelling methodologies. This research addresses the question of smaller sample sizes which constrain the use of standard regression approaches and applies a bootstrapping method which substitutes for traditional assumptions
on distributions and asymptotic results. It was found that the suburban rail demand is inelastic to fare which indicates that the revenue would increase with an increase in fare. Finally, the paper illustrates the use of computed elasticities by estimating the demand for suburban rail in Kolkata.
2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
摘要
本文分析了郊区铁路票价弹性, 并比较了印度铁路在三个城市即钦奈、加尔各答和孟买的五个郊区分部业务的结果。选择的三个城市在公共交通出行中具有高度不同的份额模式, 因此对旅行者对票价、服务水平等操作变量变化的态度提供了有趣的见解。本文对发展中国家公共交通需求的决定因素作出了贡献, 并运用了经济计量方法, 包括静态和动态建模方法。本研究解决了较小的样本大小问题, 限制了标准回归方法的使用, 并应用了一种引导方法, 替代传统的分布假设和渐近结果。结果上,收入会随着票价增加而增加, 这表明郊区铁路的需求是不弹性的。最后, 通过对加尔各答郊区铁路需求的估算, 阐述了计算弹性的应用。
2016 Elsevier 有限公司保留所有权利。
正文
1.Introduction
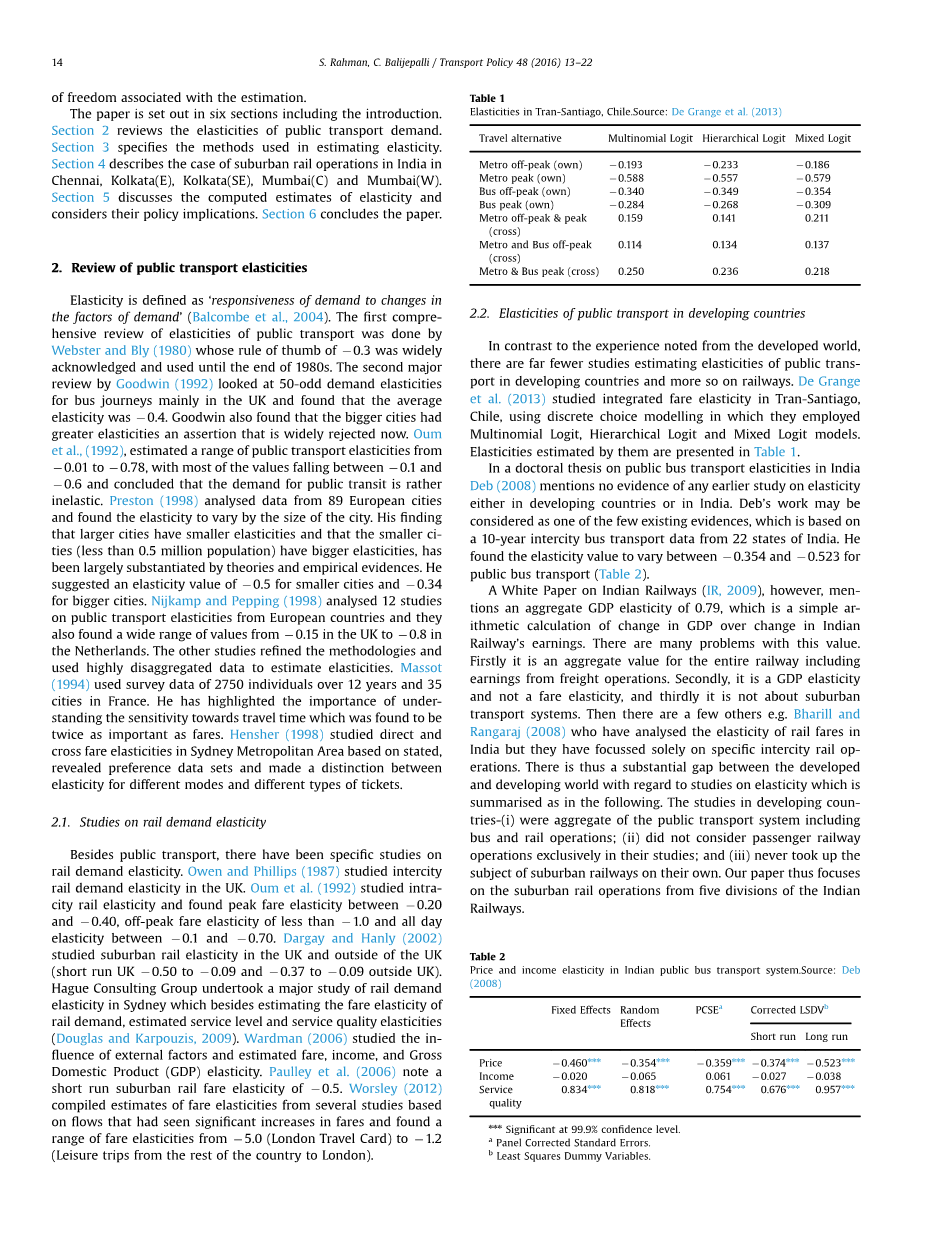
Since Transport Research Laboratory (TRL) published their report on Demand for Public Transport edited by Webster and Bly (1980), there has been an extensive research activity to understand the determinants of demand for public transport including the effect of fares, quality of service, income levels, car ownership rate, vehicle-kilometres. It is noted that the analysis of demand with respect to various factors largely remained in focus within a small group of countries having well-developed transport systems e.g. Australia, Finland, France, Netherlands, Norway, UK, USA (Bresson et al., 2003, Paulley et al., 2006). However, in the developing countries there is hardly any evidence of such research work in the past barring a few recent attempts. Currently, a number of cities in developing countries e.g. Mumbai, Delhi, Hyderabad, Bengaluru (India), Philippines (Manila), Dhaka (Bangladesh) and Jakarta (Indonesia) have all initiated metro rail systems which are in different stages of planning/execution. Notably, some of these metro rail projects involve agencies other than the governments under the public/private partnerships. Whosoever builds/owns/operates the infrastructure it will be essential to ensure the economic viability of the project but if it involves private investment it will be necessary to estimate the financial viability too, either way require a good understanding of the determinants of demand. Aside from the regulatory structure, design of the new infrastructure will also depend on the estimates of demand while arriving at a suitable specification for the system being planned.
1.简介
自从运输研究实验室 (TRL) 出版了韦伯斯特和布莱编辑的公共交通需求报告 (1980), 已经进行了广泛的研究活动, 用以了解公共交通需求的决定因素, 包括影响票价、服务质量、收入水平、汽车保有率、车辆公里数等。有人指出, 对各种因素的需求分析主要集中在有发达运输系统的少数国家, 如澳大利亚、芬兰、法国、荷兰、挪威、英国、美国(Bresson et al., 2003, Paulley et al., 2006)。然而, 在发展中国家, 除了最近几次尝试之外, 几乎没有人进行这种研究工作。目前, 一些发展中国家的城市, 例如孟买、德里、海德拉巴、班加罗尔 (印度)、菲律宾 (马尼拉)、达卡 (孟加拉国) 和雅加达 (印度尼西亚) 都已启动了地铁轨道系统, 它们处于不同的规划或者执行阶段。值得注意的是, 其中一些地铁项目涉及政府以外的机构, 属于公共与私营部门的合作关系。但凡建立、拥有亦或是经营基础设施, 就必须确保项目的经济可行性, 但如果涉及私人投资, 还有必要估计财力可行性, 无论哪种方式都需要很好地了解需求的决定因素。除了规管架构外, 新基建的设计亦会视乎需求的估计而定, 从而为计划的系统提供适当的规格。
The aim of this paper is to understand the passengersrsquo; response to fare changes in suburban railway systems with the ultimate objective of improving fare policies and managing the suburban transport system better. The main hypothesis is that the demand is related to and is explained by operational variables such as fares and service frequencies. While the demand is represented in terms of pass-km, fares are represented as yield i.e. revenue /pass-km and the frequency of operations is represented by vehicle-km as a proxy. The paper hypothesises further that the demand is also related to socio-economic variables such as population and percapita income levels besides the availability of alternative modes e.g. personal vehicles and their operating costs. Following from the literature, the paper investigates linearised relationships between the explained variable i.e. the demand and the explanatory variables including operational and socio-economic variables. The method relies on historic data obtained from Indian Railways, but as the data sets are limited to a 30- year period, this paper uses bootstrapping method to overcome the limitation of fewer degrees of freedom associated with the estimation.
本文的目的是了解旅客对城郊铁路系统票价变化的响应, 以期更好地改善票价政策和管理郊区交通系统的最终目标。主要假设是, 需求与价格和服务频率等操作变量有关, 并被解释。虽然需求以通行费的形式表示, 但票价是以收益率即收入/通过公里为代表的, 运营频率以机动车公里作为代
全文共58361字,剩余内容已隐藏,支付完成后下载完整资料
资料编号:[12216],资料为PDF文档或Word文档,PDF文档可免费转换为Word
以上是毕业论文外文翻译,课题毕业论文、任务书、文献综述、开题报告、程序设计、图纸设计等资料可联系客服协助查找。


